Business
8 Key Factors Influencing Global Economic Stability


In an increasingly interconnected world, the stability of the global economy is influenced by a multitude of factors. From the performance of financial markets to the intricacies of monetary and fiscal policies, the complex web of global economic stability is shaped by a delicate balance of variables. Understanding these key factors is essential for anyone with a vested interest in the global economy.
As we navigate the complexities of international trade, inflation rates, employment levels, and GDP growth, the interplay of these factors can have far-reaching implications.
Key Takeaways
- Financial markets and economic indicators, such as GDP growth, unemployment rates, consumer price index, and industrial production, provide insights into global economic stability.
- Monetary policy and fiscal policy play crucial roles in shaping the economic landscape, with interest rates management, quantitative easing, exchange rate management, and coordination with structural reforms being important factors.
- International trade, including trade agreements, currency exchange rates, and reduction of trade barriers, impact global economic stability and growth.
- Inflation rates and employment levels, including labor force participation, are key indicators of economic stability, with fluctuations influenced by supply chain disruptions, consumer demand shifts, government monetary policies, and their impact on consumer behavior, business decisions, and economic productivity.
Financial Markets
Analyzing the performance of financial markets reveals essential insights into the interconnectedness of global economic stability and the factors that influence it. Financial markets play a pivotal role in the allocation of resources, determination of asset prices, and the overall health of an economy. The stock market, bond market, foreign exchange market, and money market are integral components of the financial system, each with its unique dynamics and influence on the global economic landscape.
Key factors that influence financial markets and, by extension, global economic stability, include monetary policy decisions, geopolitical events, economic indicators, and market sentiment. Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve in the United States, wield significant influence through interest rate decisions and open market operations, impacting borrowing costs, investment decisions, and ultimately economic activity. Geopolitical events, such as trade wars or regional conflicts, can create volatility and uncertainty in financial markets, affecting investor confidence and capital flows. Economic indicators like GDP growth, unemployment rates, and inflation data serve as barometers for the health of an economy, shaping market expectations and investment strategies.
Understanding the intricacies of financial markets and the factors that drive their performance is crucial for policymakers, investors, and businesses seeking to navigate the complex web of global economic interdependence.
Economic Indicators
Economic indicators provide crucial quantitative and qualitative data that offer insights into the current and future state of an economy, guiding informed decision-making by policymakers, investors, and businesses. These indicators encompass a wide range of metrics, including GDP growth, unemployment rates, consumer price index (CPI), industrial production, and consumer confidence.
GDP growth reflects the overall economic health, while unemployment rates indicate labor market conditions. The CPI measures inflation, providing essential information for monetary policy decisions. Industrial production serves as a barometer for the manufacturing sector, and consumer confidence gauges the sentiment and spending patterns of households.
These indicators play a pivotal role in assessing the direction of the economy and are closely monitored by global stakeholders. For instance, central banks utilize these indicators to determine interest rates, influencing borrowing costs and economic activity. Investors rely on these metrics to make informed investment decisions, while businesses leverage them for strategic planning and risk management.
As such, economic indicators serve as critical tools for understanding the macroeconomic environment, facilitating transparency and informed decision-making in a free and open society.
Monetary Policy
The insights derived from economic indicators, such as GDP growth, unemployment rates, and the consumer price index, significantly inform the formulation and implementation of monetary policy, which plays a crucial role in shaping a country’s economic landscape.

- Interest Rates Management:
Central banks adjust interest rates to influence borrowing and spending behavior, thus impacting inflation and economic growth. Lowering interest rates encourages borrowing and spending, stimulating economic activity. Raising interest rates curbs inflation and excessive borrowing, promoting economic stability. - Quantitative Easing (QE):
Central banks engage in QE by purchasing government securities to inject liquidity into the economy. This can lower long-term interest rates, stimulating investment and consumption. However, it may also lead to asset price inflation and currency devaluation. - Exchange Rate Management:
Central banks may intervene in foreign exchange markets to stabilize or influence their currency’s value. A strong currency can lower import prices and inflation but may harm exports. A weak currency can boost exports but may increase inflation through higher import costs.
Fiscal Policy
In contemporary economic landscapes, fiscal policy, as a critical tool wielded by governments, exerts substantial influence on overall economic stability and growth. Fiscal policy encompasses government decisions regarding taxation and public expenditure to achieve desired economic outcomes.
In recent times, the global economic environment has witnessed diverse approaches to fiscal policy, reflecting the varying priorities and challenges faced by different countries. For instance, some nations have implemented expansionary fiscal policies characterized by increased government spending and tax cuts to stimulate economic activity and employment. On the other hand, certain countries have pursued contractionary fiscal policies aimed at reducing budget deficits and curbing inflationary pressures.
The effectiveness of fiscal policy in promoting economic stability and growth is underscored by its ability to influence aggregate demand, investment, and consumer behavior. Moreover, the coordination of fiscal policy with monetary policy and structural reforms is pivotal in achieving sustainable and inclusive growth.
As the global economic landscape continues to evolve, the role of fiscal policy in shaping the trajectory of national and global economies remains a subject of ongoing analysis and debate.
International Trade
Amidst the dynamics of fiscal policy considerations, the intricate interplay of international trade policies on global economic stability warrants careful examination. International trade plays a pivotal role in shaping the economic landscape, influencing growth, and fostering cooperation among nations.


Several key factors influence the impact of international trade on global economic stability:
- Trade Agreements: The nature and scope of trade agreements between nations significantly impact global economic stability. The terms of these agreements, including tariffs, quotas, and trade facilitation measures, can either promote or hinder international trade, thereby affecting the overall economic stability.
- Currency Exchange Rates: Fluctuations in currency exchange rates have a profound impact on international trade and economic stability. Exchange rate movements influence the competitiveness of exports and imports, thus shaping trade balances and overall economic stability.
- Trade Barriers: The presence of trade barriers, such as tariffs and non-tariff barriers, can impede the flow of goods and services across borders, affecting economic stability. The reduction of trade barriers through mutual agreements can lead to increased economic stability and growth.
Understanding the intricate dynamics of international trade is essential for ensuring global economic stability and fostering an environment conducive to freedom and prosperity.
Inflation Rates
An analysis of inflation rates provides crucial insights into the economic landscape, offering valuable indicators of price stability and purchasing power.
In recent months, global inflation rates have witnessed fluctuations, influenced by factors such as supply chain disruptions, shifts in consumer demand, and government monetary policies.
The International Monetary Fund’s World Economic Outlook database indicates that as of September 2021, advanced economies experienced an average inflation rate of around 2.5%, while emerging market and developing economies faced a slightly higher average of approximately 4.8%.
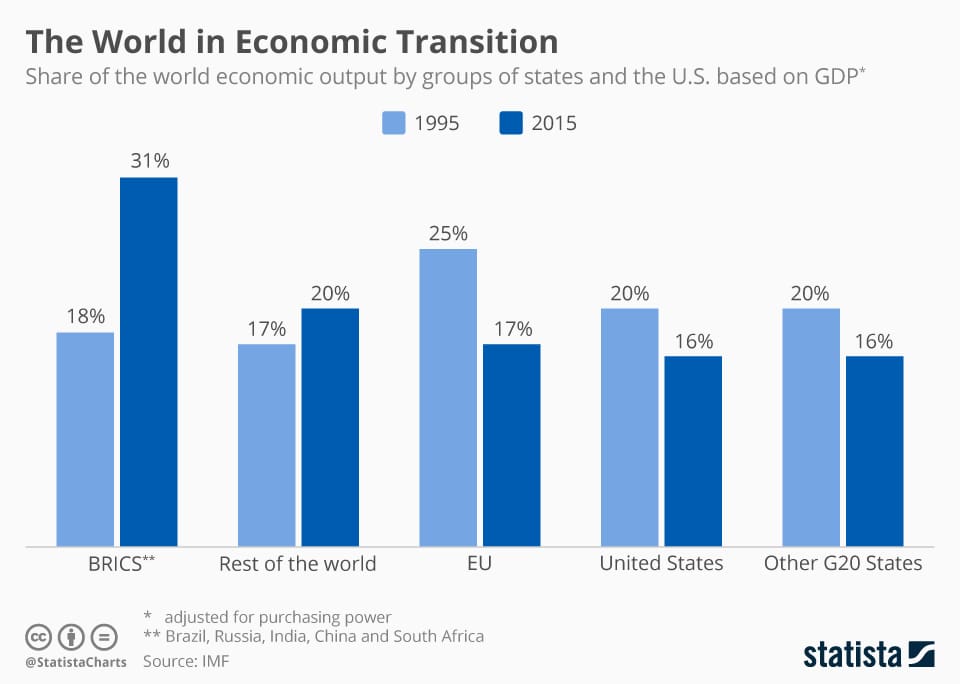

These variations can impact consumer behavior, business investment decisions, and overall economic growth prospects.
Central banks play a pivotal role in managing inflation rates through mechanisms such as interest rate adjustments and open market operations. However, it is imperative to strike a balance between controlling inflation and supporting economic recovery, especially in the aftermath of significant global events.
As the world navigates through these challenges, it becomes essential for policymakers, businesses, and individuals to closely monitor inflation dynamics and adapt strategies to mitigate its potential adverse effects on economic stability and freedom of choice.
Employment Levels
The employment levels in a country are crucial indicators of its economic stability. Factors such as unemployment rates and labor force participation play a significant role in determining the overall health of an economy.
Analyzing these metrics provides valuable insights into the workforce dynamics and the potential impact on the country’s economic stability.


Unemployment Rates
The unemployment rates of a country are a key metric in assessing the health of its economy, providing valuable insights into the labor market dynamics and overall economic stability.
- Labor Force Participation: A high unemployment rate may indicate a shrinking labor force, potentially signaling discouraged workers or demographic shifts.
- Industry Disparities: Variations in unemployment rates across industries can reveal structural economic challenges or advancements.
- Policy Implications: Unemployment rates influence fiscal and monetary policies, as well as social welfare programs, making them a crucial consideration for policymakers.
These factors underscore the significance of monitoring and addressing unemployment rates to ensure economic freedom and prosperity.
Labor Force Participation
Labor force participation, a critical measure of employment levels, reflects the engagement of the working-age population in the labor market and is essential in evaluating the overall economic productivity and potential of a country.
Currently, global labor force participation rates vary significantly, influenced by factors such as demographic shifts, cultural norms, and government policies.
High participation rates can indicate a robust economy, as more people are actively contributing to the workforce, potentially boosting productivity and innovation.


On the other hand, low participation rates may signify underutilization of human capital and can hinder economic growth.
Understanding the nuances of labor force participation is crucial for policymakers and businesses, as it directly impacts the availability of skilled labor, consumer spending power, and ultimately, the economic stability and prosperity of a nation.
GDP Growth
Amidst the complex web of global economic indicators, GDP growth stands as a pivotal measure of a nation’s economic health and trajectory. The rate of GDP growth reflects the overall expansion or contraction of an economy and is a key determinant of living standards, employment levels, and investment opportunities.
Several key factors currently influencing GDP growth include:
- Monetary Policy: Central banks’ decisions on interest rates and money supply significantly impact borrowing costs, consumer spending, and business investment, thus affecting GDP growth.
- Trade Dynamics: Tariffs, trade agreements, and global supply chain disruptions can all influence a nation’s export-import balance, impacting GDP growth.
- Fiscal Policy: Government spending, taxation, and budget deficits or surpluses play a crucial role in shaping overall demand and investment, thereby influencing GDP growth.
These factors, among others, are integral in shaping a nation’s economic performance and can serve as essential indicators for policymakers and businesses seeking to understand and navigate the complex landscape of global economic stability.

Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Geopolitical Tensions and Conflicts Impact Global Economic Stability?
Geopolitical tensions and conflicts can disrupt global economic stability by increasing uncertainty, affecting trade, and driving up commodity prices. Investor confidence may wane, leading to market volatility and reduced international cooperation.
What Role Do Environmental and Sustainability Factors Play in Influencing Global Economic Stability?
Environmental and sustainability factors are increasingly shaping global economic stability. From resource scarcity to climate change impacts, these variables influence industries, supply chains, and investment decisions. Their integration into economic strategies is critical for long-term viability.
How Do Technological Advancements and Innovation Affect Global Economic Stability?
Technological advancements and innovation significantly impact global economic stability by driving productivity gains, fostering efficiency, and creating new industries. They also influence trade patterns, labor markets, and consumer behavior, shaping the overall economic landscape.
What Are the Potential Impacts of Global Health Crises on Economic Stability?
In times of global health crises, the potential impacts on economic stability can be profound. These crises can disrupt supply chains, reduce consumer confidence, and strain healthcare systems, leading to economic downturns and increased volatility in financial markets.
How Do Social and Cultural Factors Contribute to Global Economic Stability?
Social and cultural factors play a significant role in global economic stability. They influence consumer behavior, labor force dynamics, and trade patterns. Understanding these factors is essential for crafting policies that promote sustainable economic growth and resilience.




Hi, I’m Kyle Rivera, a news journalist and blog editor with the Daily Evening News. A TCU alum with a flair for storytelling, I spend my days uncovering impactful stories and my evenings exploring the realms of yoga, cycling, and whimsically bad poetry.
Travel is my escape; I’ve trekked from Tokyo’s neon lights to Iceland’s tranquil vistas. But no journey is complete without Mogli, my Golden Retriever, who’s redefining his breed standards in the most charming ways.
I love connecting with fellow travelers, yogis, cyclists, and anyone who enjoys a laugh at my poetic attempts. If you’re into stories that inspire, travel escapades, or just want to see what Mogli and I are up to, I’d love to hear from you on Instagram or Facebook. Let’s share tales and tips from around the globe!

